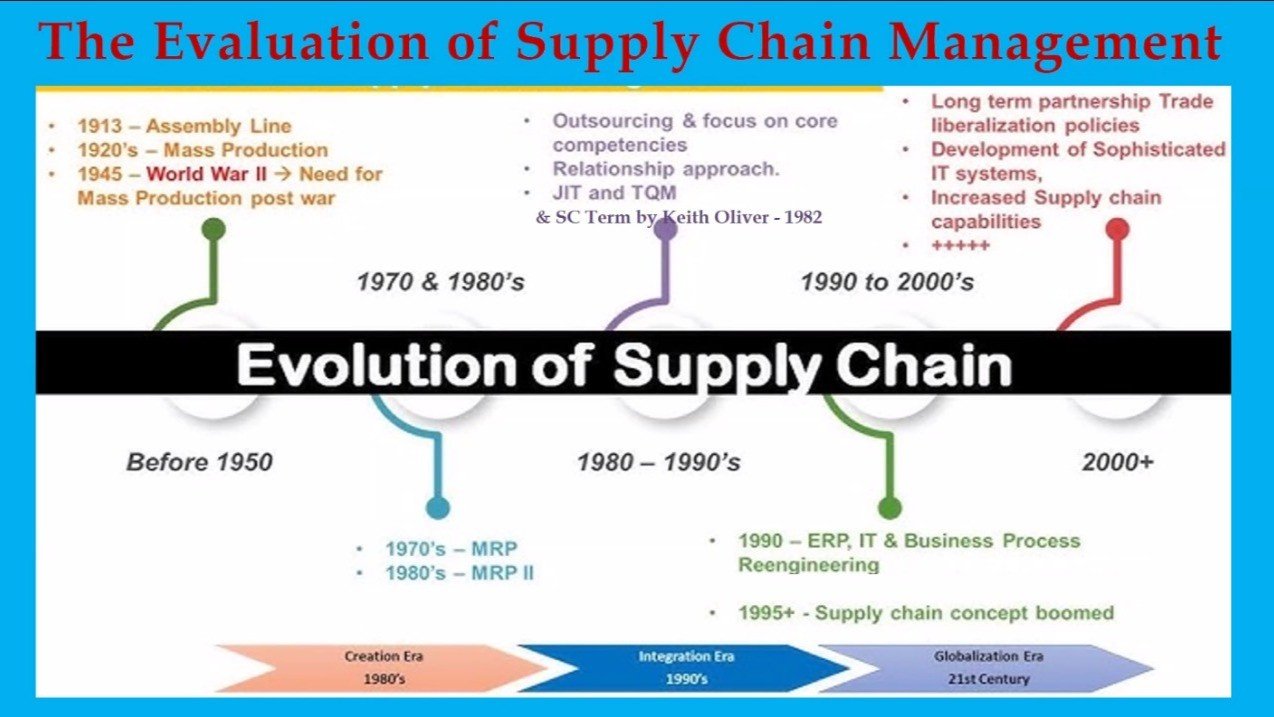
In today’s fast-paced business world, two key terms often come up when discussing company processes: Supply Chain Management (SCM) and Operations Management (OM). While they are closely related, they have distinct roles and functions in any organization. Here’s a simple breakdown to help you understand their differences.

What is Supply Chain Management (SCM)?
SCM focuses on the flow of goods, services, and information across the entire supply chain, from the raw materials supplier to the end customer. It is about managing relationships with external entities to ensure the product or service reaches the customer efficiently.
Key Functions of SCM:
1. Inbound Logistics: Procuring raw materials and managing transportation to the company.
2. Outbound Logistics: Delivering finished products to customers.
3. Procurement: Sourcing goods and materials at the best possible terms.
4. Technology and Information Flow: Sharing data with suppliers and customers for smooth operations.
Goal of SCM: To ensure products and services are delivered to customers in the right quantity, at the right time, and with minimal cost.
What is Operations Management (OM)?
OM focuses on the internal processes within a company that turn inputs (like materials, labor, and technology) into outputs (finished goods or services). It is concerned with the efficiency and effectiveness of internal operations.
Key Functions of OM:
1. Production Planning: Ensuring optimal use of resources to meet demand.
2. Quality Management: Maintaining product or service quality.
3. Capacity Planning: Managing production capacity to avoid bottlenecks.
4. Workforce Management: Overseeing employee roles and performance.
Goal of OM: To maximize productivity and ensure high-quality outputs while minimizing costs.
The Key Difference
While SCM looks at the big picture and manages the flow of goods and information across multiple entities, OM focuses on what happens within the organization. Think of SCM as the “external engine” that moves resources across a network and OM as the “internal engine” that converts resources into finished products.
An Analogy:
If a company is like a car, SCM is the navigation system that plans the best route (external coordination), while OM is the engine ensuring the car moves efficiently (internal processes).
—
How They Work Together
SCM and OM are interdependent. SCM ensures the company gets the materials needed to operate, while OM ensures those materials are used effectively. Together, they ensure that the customer gets the right product, at the right time, and at the right quality.
—
Conclusion
Both SCM and OM are vital for a company’s success. SCM ensures smooth external coordination, while OM focuses on internal efficiency. Understanding their roles helps businesses streamline processes and improve customer satisfaction.
If you’re managing a business or studying these areas, it’s important to see how they complement each other and contribute to overall success.
What are your thoughts on SCM and OM? Feel free to share your perspective in the comments!